
Take Action to Lower Your Breast and Ovarian Cancer Risk
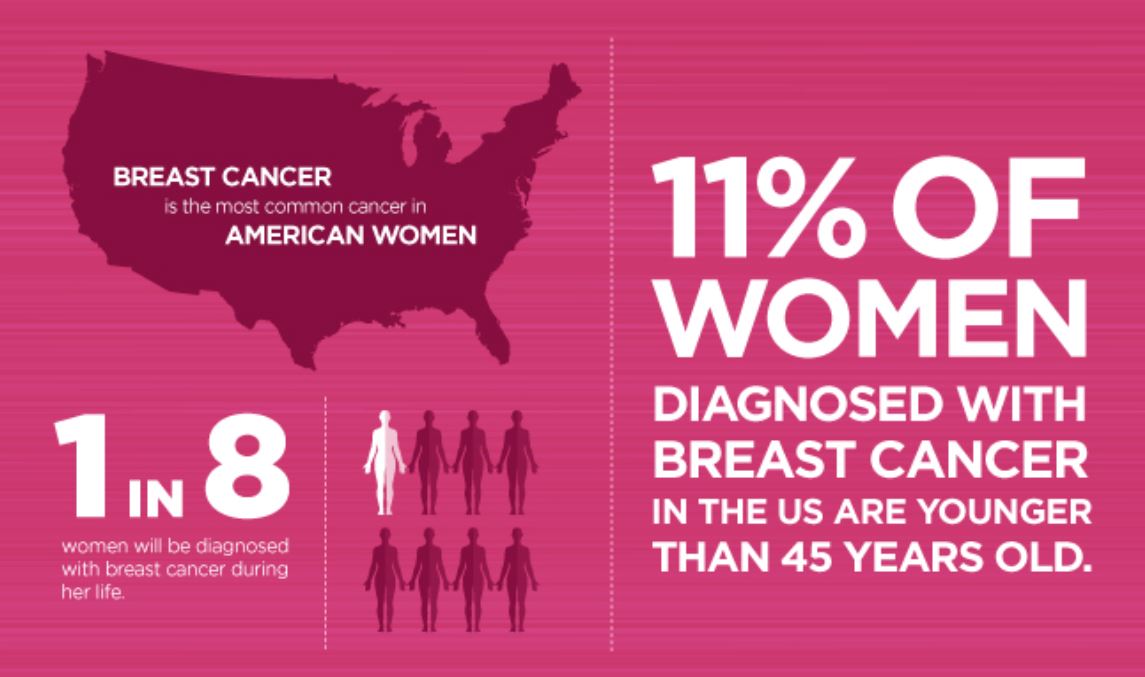
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the United States. While breast cancer mostly occurs among older women, in rare cases breast cancer does affect women under the age of 45. Eleven percent of all cases of breast cancer in the U.S. are reported in this age group.
Breast cancer in young women is—
- More likely to be hereditary than breast cancer in older women.
- More likely to be found at a later stage, and is often more aggressive and difficult to treat.
- Often coupled with unique issues, including concerns about body image, fertility, finances, and feelings of isolation.
All women are at risk for getting breast cancer, but some things can raise a woman’s risk for getting breast cancer before age 45.
Take Action to Lower Your Breast and Ovarian Cancer Risk
Knowing your cancer risk and being proactive about your health may help you take steps to lower your risk for getting breast or ovarian cancer, or find it at an early stage.
Learn Your Family History of Cancer
Asking relatives about their cancer histories can be hard. Follow these tips:
- Share that you have learned that cancers can run in families.
- Explain that you are creating a record of your family’s history of cancer.
- Encourage family members to respond in a way that is most comfortable to them.
- Word your questions carefully, be a good listener, and respect their privacy.
- Write down who had cancer, age when diagnosed, and type of cancer.
Understand Genetic Counseling and Testing
Genetic counseling and testing are recommended for women whose family medical history has certain patterns of cancer.
What is Genetic Counseling?
Genetic counseling can help you understand your risk based on your personal and family medical history.
You will discuss things like:
- If a genetic test is right for you.
- Specific tests that might be used and their accuracy.
- Possible genetic test results and next steps.
- How a test result might not give you all the information you need.
- The emotional risks and benefits of genetic testing.
- How genetic test results may affect other family members.
Did You Know? Inherited mutations are thought to play a role in 5-10% of breast and 10-15% of ovarian cancers.
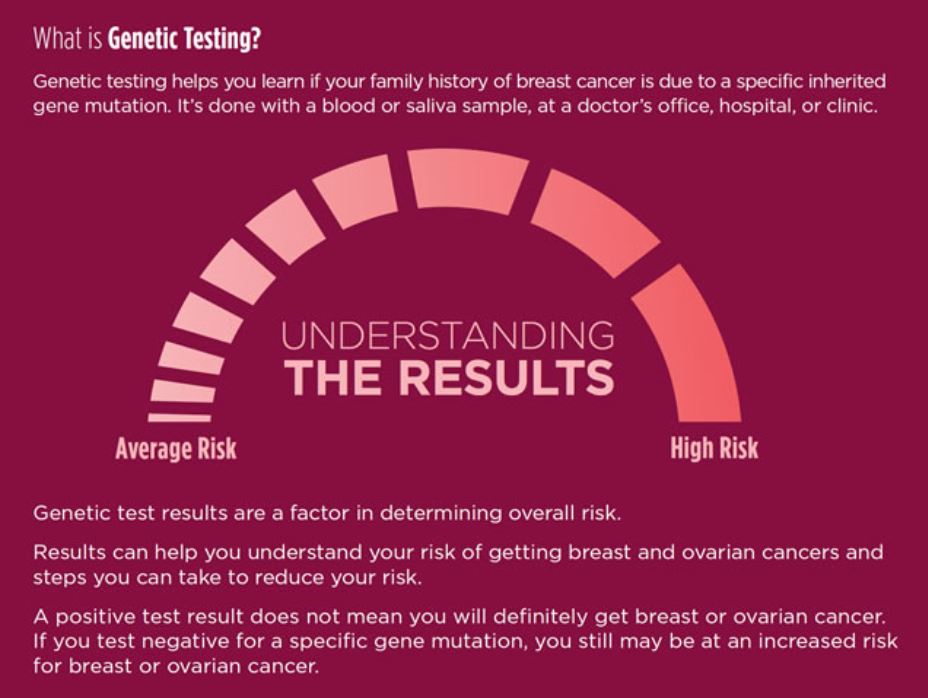
What is Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing helps you learn if your family history of breast cancer is due to a specific inherited
gene mutation. It’s done with a blood or saliva sample, at a doctor’s office, hospital, or clinic.
Genetic test results are a factor in determining overall risk.
Results can help you understand your risk of getting breast and ovarian cancers and steps you can take to reduce your risk.
A positive test result does not mean you will definitely get breast or ovarian cancer. If you test negative for a specific gene mutation, you still may be at an increased risk for breast or ovarian cancer.
Make Healthy Lifestyle Changes
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Get enough physical activity
- Breastfeed your babies
Increase the chance of finding breast cancer early, when it’s easier to treat.
- Know how your breasts normally look and feel.
- Talk to your doctor right away if you notice changes in your breast.
- Talk to your doctor if you have a higher risk, including a family history of cancer.
Source:
- CDC
Graphic:
- CDC





Most Commented