
Breast Cancer Awareness Month

According to CDC, each year in the United States, more than 240,000 women get breast cancer and more than 40,000 women die from the disease. Men also get breast cancer, but it is not very common. Less than 1% of breast cancers occur in men.
Most breast cancers are found in women who are 50 years old or older, but breast cancer also affects younger women. About 10% of all new cases of breast cancer in the United States are found in women younger than 45 years of age.
What Is Breast Cancer?
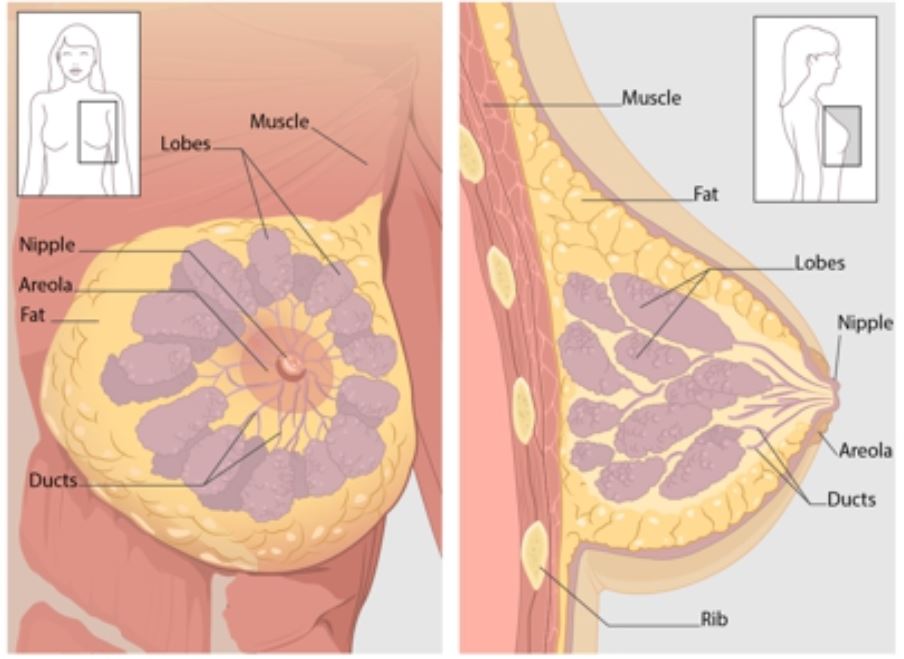
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
The most common kinds of breast cancer are:
Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
What Are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
Different people have different symptoms of breast cancer. Some people do not have any signs or symptoms at all.
Some warning signs of breast cancer are:
-
-
-
- New lump in the breast or underarm (armpit).
- Thickening or swelling of part of the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Redness or flaky skin in the nipple area or the breast.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area.
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk, including blood.
- Any change in the size or the shape of the breast.
- Pain in any area of the breast.
-
-
Keep in mind that these symptoms can happen with other conditions that are not cancer.If you have any signs or symptoms that worry you, be sure to see your doctor right away.
What Can I Do to Reduce My Risk of Breast Cancer?
Many factors over the course of a lifetime can influence your breast cancer risk. You can’t change some factors, such as getting older or your family history, but you can help lower your risk of breast cancer by taking care of your health in the following ways:
-
-
-
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Don’t drink alcohol, or limit alcoholic drinks to no more than one per day.
- If you are taking, or have been told to take, hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives (birth control pills), ask your doctor about the risks and find out if it is right for you.
- Breastfeed your children, if possible.
- If you have a family history of breast cancer or inherited changes in inherited changes in your BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your risk.
-
-
Staying healthy throughout your life will lower your risk of developing cancer, and improve your chances of surviving cancer if it occurs.
What Is Breast Cancer Screening?
Breast cancer screening means checking a woman’s breasts for cancer before there are signs or symptoms of the disease.
Although breast cancer screening cannot prevent breast cancer, it can help find breast cancer early, when it is easier to treat. Talk to your doctor about which breast cancer screening tests are right for you, and when you should have them.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that women who are 50 to 74 years old and are at average risk for breast cancer get a mammogram every two years. Women who are 40 to 49 years old should talk to their doctor or other health care professional about when to start and how often to get a mammogram. Women should weigh the benefits and risks of screening tests when deciding whether to begin getting mammograms before age 50.
There are three tests that used by health care providers to screen for breast cancer:
Mammogram
A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast. Mammograms are the best way to find breast cancer early when it is easier to treat and before it is big enough to feel or cause symptoms. Having regular mammograms can lower the risk of dying from breast cancer. At this time, a mammogram is the best way to find breast cancer for most women.
Clinical breast exam (CBE)
A clinical breast exam is an examination by a doctor or nurse, who uses his or her hands to feel for lumps or other changes.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A breast MRI uses magnets and radio waves to take pictures of the breast. MRI is used along with mammograms to screen women who are at high risk of getting breast cancer. Because breast MRIs may appear abnormal even when there is no cancer, they are not used for women at average risk.
How Is Breast Cancer Treated?
Breast cancer is treated in several ways. It depends on the kind of breast cancer and how far it has spread. People with breast cancer often get more than one kind of treatment.
-
-
-
- Surgery. An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.
- Chemotherapy. Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer cells. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
- Hormonal therapy. Blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow.
- Biological therapy. Works with your body’s immune system to help it fight cancer cells or to control side effects from other cancer treatments.
- Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer cells.
-
-
Doctors from different specialties often work together to treat breast cancer. Surgeons are doctors who perform operations. Medical oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with medicine. Radiation oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with radiation.
Source:
- CDC
- National Cancer Institute


Most Commented