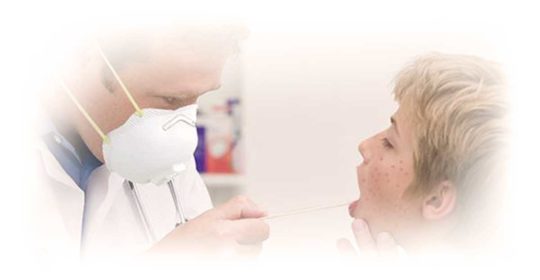
Prevent Measles Through Vaccination
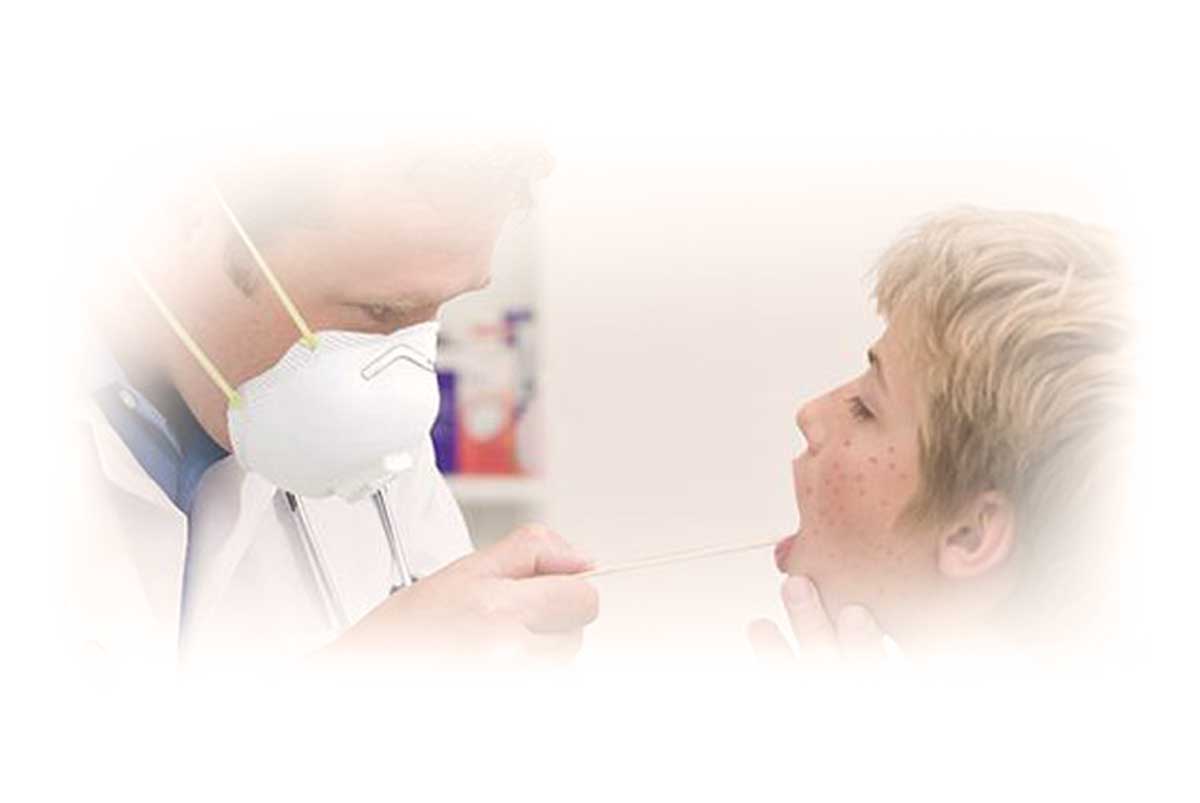
Measles, also called Rubeola, is a highly contagious viral disease. The disease is no longer common in the United States, however it is widespread in many parts of the world including Europe, Africa, and Asia.
Measles starts with fever, runny nose, cough, red eyes, and sore throat. It’s followed by a rash that spreads over the body. Measles virus is highly contagious virus and spreads through the air through coughing and sneezing. Make sure you and your child are protected with measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
Measles remains a common disease in many parts of the world, including areas in Europe, Asia, the Pacific, and Africa. Worldwide, about 20 million people get measles each year; about 146,000 die. In the United States, most of the measles cases result from international travel. The disease is brought into the United States by unvaccinated people who get infected in other countries. They spread measles to others, which can cause outbreaks.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of getting infected when they travel internationally.
Measles Q&A
Download State of Georgia’s Department of Health Q&A sheet about Measles
Read More:
- Top 4 Things Parents Need to Know about Measles (CDC – http://www.cdc.gov/measles/about/parents-top4.html)
- For Travelers (http://www.cdc.gov/measles/travelers.html)


Most Commented